7 Major Challenges Facing the Healthcare Industry in 2026

Behind every breakthrough in healthcare lies a set of stubborn challenges that providers cannot ignore. Rising operational costs, critical staffing shortages, and increasing cybersecurity risks make innovation difficult to sustain. Add shifting patient expectations and new compliance standards, and the path forward looks far from simple.
This article examines seven challenges at the heart of healthcare’s struggle to strike a balance between progress and practicality.
Rising Costs and Inflation
Healthcare costs continue rising at a rate that stresses both providers and patients. In the 12 months ending August 2025, healthcare prices in the U.S. rose about 3.4%, compared with the overall inflation rate near 3.0%. Key cost pressures now include:
- Prescription Drug Prices: New drug list prices more than doubled between 2021 and 2024, largely driven by treatments for rare diseases. The median annual list price for a newly launched drug surpassed $370,000 in 2024. Also, drug prices rose three times faster than overall inflation since the mid-2010s.
- Labor Costs: Hospitals now spend just over 56% of total costs on compensation and related expenses for staff. Shortages of qualified healthcare workers plus rising wages and benefits continue pushing that number upward.
- Medical Services and Hospital Expenses: Prices for hospital services have increased significantly, especially in outpatient and inpatient settings. In a recent analysis, hospital and related services rose 7.7% year over year for certain categories, well above general medical care inflation.
Several strategies show promise in mitigating this trend. Applying advanced automation, such as AI and machine learning in administrative and billing workflows may reduce overhead and lower labor demands. Enhancing transparency in pricing helps consumers compare costs and make informed decisions. Encouraging value-based payment models rewards outcomes and efficiency rather than volume of services delivered.
Cybersecurity
The growing reliance of healthcare organizations on digital infrastructure has elevated the risk of cyberattacks. Sensitive patient data, including medical records and financial information, represents a prime target for malicious actors. Successful breaches can result in data compromises, operational disruptions, and substantial financial losses.
As more healthcare functions move online over the next year – like an increase in digital patient statements adoption – it’s extremely important to ensure these processes are protected from outside threats.
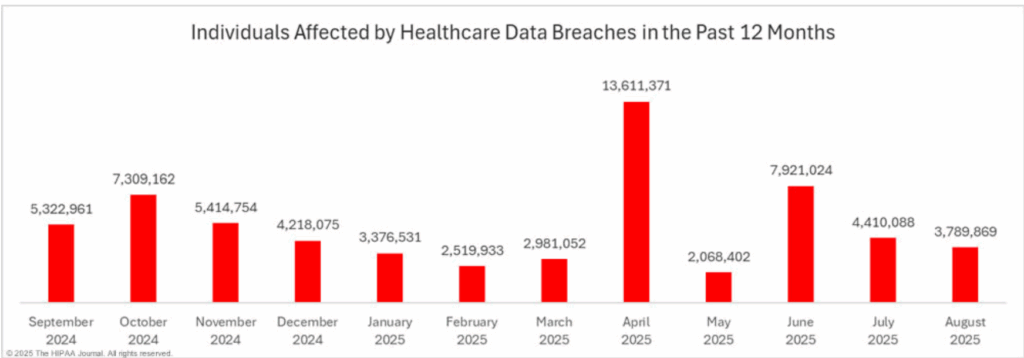
The prevalence of cyberattacks within healthcare will persist due to the industry’s slow response to emerging threats and the inherent vulnerabilities of decentralized systems. A data breach not only compromises sensitive patient information but also incurs significant financial penalties for non-compliance with industry regulations.
To mitigate these risks, healthcare providers are increasingly investing in robust cyber-resilience measures. Implementing multi-factor authentication and strong firewalls are essential steps in reducing vulnerability to cyberattacks. Additionally, requiring third-party vendors to hold a HITRUST certification, which encompasses a comprehensive set of security standards, can significantly lower the risk of ransomware attacks and data breaches.
Invoicing and Payment Processing
Patients now shoulder a larger share of healthcare costs, making collections an increasingly complex challenge for practices. By offering flexible payment options and aligning with patient expectations, providers can reduce delays while fostering trust.
Adopting digital communications — such as patient estatements — and a variety of payment methods, including chat2pay, mobile payments, and payment plan options, can significantly improve patient satisfaction and streamline the payment process. Utilizing text message alerts and reminders further enhances communication and reinforces financial obligations.

Implementing a robust patient billing system in-house can be both costly and time-consuming. By partnering with a provider specializing in cloud-based billing solutions, healthcare practices can access cutting-edge technology without the need for significant investments or administrative overhead. This approach ensures compliance with data privacy regulations while delivering a seamless and efficient payment experience for patients.
Healthcare Workforce Shortages
The healthcare industry is facing a growing labor crisis of workforce shortages, particularly for nurses and physicians. This shortage is leading to longer wait times, reduced access to care, and potential impacts on the quality of care. Several factors contribute to this shortage, including:
- Aging Population: The increasing number of older adults requires more healthcare services, further straining the existing workforce.
- Burnout and Turnover: High rates of burnout and turnover among healthcare professionals are exacerbating the shortage. Factors such as heavy workloads, long hours, and emotional stress contribute to burnout, leading many to leave the profession.
- Retirement: As the baby boomer generation ages and retires, there is a wave of experienced healthcare professionals leaving the workforce. This creates a gap in the supply of skilled workers.
- Inadequate Supply of Graduates: The number of graduates from healthcare programs, such as nursing and medical schools, is not keeping pace with the growing demand for healthcare services. This shortage is particularly acute in certain specialties and geographic regions.
To attract and retain healthcare professionals, substantial improvements in working conditions, training, and resources are crucial. Leveraging telehealth and remote care can also help alleviate workload pressures and enhance job satisfaction.
Aging Population
The global population is aging rapidly, with a significant increase in the number of older adults. This demographic shift has profound implications for healthcare systems, which must adapt to meet the unique needs of an aging population. Some key trends to consider:
- Increasing Lifespan: People are living longer, with life expectancy increasing in many countries. This is due to factors such as improved healthcare, better living conditions, and advancements in medical technology.
- Growing Proportion of Older Adults: The proportion of the population aged 65 and older is steadily increasing. This trend is particularly pronounced in developed countries.
- Chronic Disease Burden: Older adults are more likely to suffer from chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and dementia. These conditions require ongoing care and management.
To address the challenges posed by an aging population, healthcare systems must adopt a proactive and comprehensive approach, including leveraging technology — such as telehealth and remote monitoring, and improving preventative care.
Regulatory Changes
Constantly shifting regulations shape nearly every aspect of healthcare delivery. Success depends on anticipating these shifts, adjusting processes, and strengthening compliance systems to reduce risk while upholding patient care standards. Over the next year, several regulatory challenges warrant close focus:
- Antitrust Laws: Healthcare providers must also be aware of antitrust laws that prohibit anticompetitive practices, such as mergers and acquisitions that reduce competition.
- Data Privacy Laws: The protection of patient data is a top priority, and healthcare providers must comply with various data privacy laws, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. These laws impose strict requirements for safeguarding patient information and preventing data breaches.
- Interoperability Standards: Ensuring interoperability between healthcare systems is essential for seamless data exchange and patient care coordination. Adhering to interoperability standards, such as the ONC Health IT Certification Criteria, is crucial for providers to connect with other healthcare organizations and exchange patient information electronically.
- Value-Based Payment Models: The shift towards value-based payment models is transforming the way healthcare providers are reimbursed. These models emphasize quality of care over quantity of services, requiring providers to demonstrate positive patient outcomes and efficient use of resources.
- Telehealth Regulations: The growing use of telehealth has led to new regulatory considerations. Ensuring compliance with telehealth regulations, including licensing requirements and patient privacy standards, is essential for providers offering virtual care services.
- Drug Pricing and Reimbursement: The pricing and reimbursement of pharmaceuticals continue to be a major regulatory issue. Governments and payers are seeking to control drug costs and promote affordable access to medications.
By proactively addressing regulatory challenges, healthcare providers can mitigate risks, maintain compliance, and deliver high-quality care.
Technological Advancements and Integration
Innovations such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and telehealth are presenting new opportunities to improve patient care, enhance efficiency, and reduce costs. However, the adoption and integration of these technologies also pose significant challenges.

Several technological forces now reshape healthcare delivery and operations:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI drives advances in medical imaging, drug discovery, and clinical decision-making. By processing immense datasets, algorithms detect subtle patterns, predict outcomes, and enable more precise diagnoses alongside personalized treatment strategies.
- Machine Learning: As a specialized branch of AI, machine learning refines predictions by training on large, complex datasets. Its applications include medical image interpretation, drug development pipelines, and predictive modeling that informs both individual care and population health.
- Telehealth: Remote care platforms gained lasting traction after the pandemic. They provide patients with timely access to clinicians, especially in rural and underserved regions, while reducing the need for in-person visits.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): EHR systems now anchor modern clinical practice, centralizing patient information for seamless access across providers. When effectively implemented, they enhance coordination, reduce errors, and strengthen population-level insights.
Adopting these tools demands significant investment in infrastructure, workforce training, and change management. Organizations that expand technology usage must also guard against rising threats to data security and patient privacy. Building robust protections, from encryption to continuous monitoring, ensures innovation does not undermine trust.
Final Thoughts
Healthcare enters 2026 under mounting pressure from rising costs, workforce shortages, rapid technological shifts, and evolving regulations. Meeting these challenges will demand creative strategies, cross-sector collaboration, and a relentless focus on patient outcomes. Organizations that act decisively can strengthen both affordability and sustainability while continuing to deliver care that meets the highest standards.
Partner with MailMyStatements to transition your practice’s billing operations to a personalized cloud platform. Our comprehensive solutions enable your team to focus on delivering exceptional patient care while we handle the complexities of revenue cycle management. Get in touch with us today.
LEARN MORE ABOUT HOW OUR SOLUTIONS CAN SAVE YOU TIME AND MONEY!
![]()



